Ultrasound diagnostics
The Department is equipped with the state-of-the-art modern medical equipment of the world's leading manufacturers, tailored to the needs of clinical and scientific departments in the studies of all organs and systems for early diagnosis, dynamic monitoring, treatment control, research in sports medicine.
The Department is equipped with expert - class equipment-ultrasound scanners Logiq E9, Vivid E9, Voluson E6 with all sensors that allows you to solve various diagnostic tasks.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, gallbladder with determination of function of kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneal space, prostate and bladder with determination of residual urine;
- Transrectal US of the prostate, bladder, scrotum, thyroid, mammary glands, salivary glands, lymph nodes, eyeball, orbit and appendage of the eye, pelvic organs (transabdominal and transvaginal);
- Ultrasound of the uterus and fetus;
- Doppler examination of utero-placental blood flow vessels, joints, pleural cavities, soft tissues;
- Duplex scanning of brachiocephalic vessels, transcranial duplex scanning, duplex examination of peripheral vessels (arteries and veins), duplex examination of renal vessels, duplex examination of aorta abdominal region and its branches;
- Echocardiography

The functional diagnostics of our Department offers a wide range of modern techniques, enabling you to study the state of various organs and systems, to identify violations even before the development of anatomical changes in the body.
Modern computer equipment makes it possible to conduct studies at the highest diagnostic level: to perform automatic processing of information, to determine a wide range of indicators and to form a graphic image of the obtained parameters. Methods of functional diagnostics have no contraindications for medical prescription are relatively simple in execution, and, most importantly, have sufficient accuracy and objectivity of the results.
The survey will help determine the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases or identify them at the earliest stages. Timely treatment will prevent serious complications such as stroke, myocardial infarction, heart and kidney failure.
- multiple multichannel electrocardiographs;
- modern electroencephalograph with software;
- bicycle ergometer;
- computer systems for handling the daily (Holter) monitoring of the electrocardiogram;
- computer spirograph;
- vibrometer.
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- daily ECG monitoring (Holter monitoring);
- echocardiography with dopplerography (ECHOCG);
- stress echocardiography; Bicycle ergometry (load test);
- determination of the function of external respiration (spirography);
- electroencephalography (EEG);
- vibration testing.
ECG is the most accessible and common method of examination, used mainly in cardiology. It is also successfully used in the study of patients with diseases of the lungs, kidneys, liver, endocrine glands, etc.
- Rhythm and conduction disorders (rhythm and conduction disorders are noted in people suffering from coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, are detected in endocrine diseases, violations of the blood electrolyte balance due to chronic renal failure, etc.);
- Hypertrophy (increase in the thickness of the walls of the Atria and ventricles) associated with arterial hypertension, cardiomyopathy, amyloidosis, etc;
- Myocardial ischemia (violation of blood supply to the heart) associated with coronary heart disease;
- Myocardial injury, necrosis or myocardial infarction (acute myocardial blood supply disorder);
- ECG changes in pulmonary embolism and acute pulmonary heart disease, heart defects, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, nephritis, etc.

Daily ECG monitoring is mainly used to diagnose various rhythm and conduction disorders that cannot always be registered on a standard resting ECG (transient rhythm and conduction disorders) as well as to detect and confirm coronary heart disease, including pain-free myocardial ischemia, which is a very important criterion, since a person does not feel pain, and therefore does not know about his disease, and this increases the risk of myocardial infarction and sudden death. Repeated ECG monitoring is performed to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
 Echocardiography is the most important method in the diagnosis of congenital and acquired heart defects, cardiomyopathies, pericarditis, myocarditis, chronic and acute pulmonary heart disease, blood clots, heart tumors, etc. In combination with other diagnostic methods, Echocardiography plays an important role in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and its complications – myocardial infarction — it allows you to see areas of the heart muscle with impaired contractility caused by ischemia or tissue necrosis, detect heart aneurysms as well as such terrible complications of myocardial infarction as heart muscle ruptures, thrombosis of the heart cavities, etc., requiring urgent measures, including surgical ones.
Echocardiography is the most important method in the diagnosis of congenital and acquired heart defects, cardiomyopathies, pericarditis, myocarditis, chronic and acute pulmonary heart disease, blood clots, heart tumors, etc. In combination with other diagnostic methods, Echocardiography plays an important role in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and its complications – myocardial infarction — it allows you to see areas of the heart muscle with impaired contractility caused by ischemia or tissue necrosis, detect heart aneurysms as well as such terrible complications of myocardial infarction as heart muscle ruptures, thrombosis of the heart cavities, etc., requiring urgent measures, including surgical ones.
Doppler imaging in various modes allows you to perform a qualitative and quantitative analysis of intracardiac blood flow: to assess the speed of blood flow through the valve openings, the degree of valvular insufficiency, the presence of pathological blood discharges between the cavities of the heart, to calculate cardiac output, to assess the function of contractility etc.
Bicycle ergometry is a test performed on a stationary bicycle that is adapted to perform a metered increasing load and taking into account the units of load power (in watts). During this test, the patient pedals a bicycle against of constant recording background of electrocardiogram and blood pressure measurement under the constant supervision of the doctor.
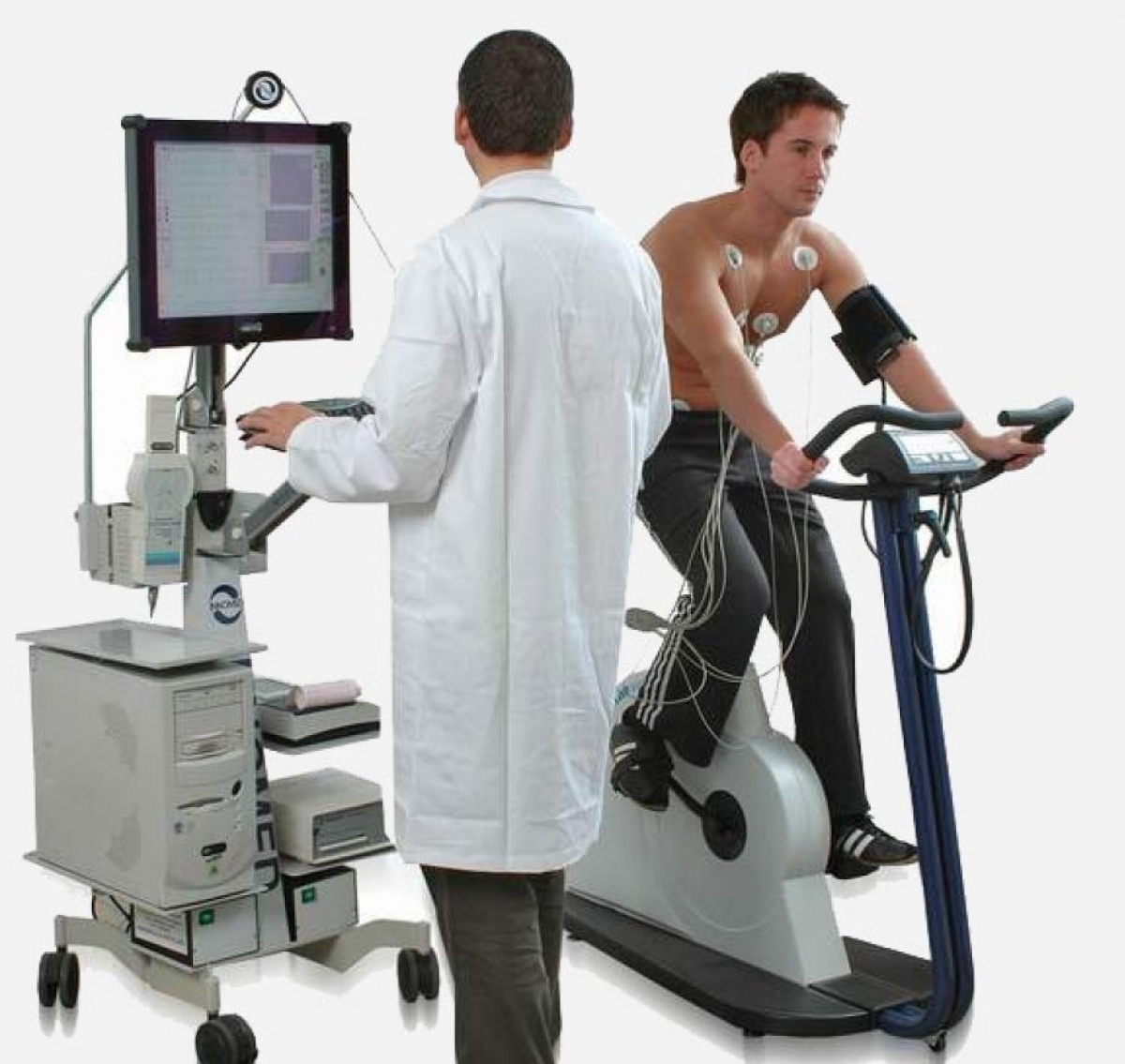
Stress echocardiography is an informative technique for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease that includes not only constant monitoring of changes in the patient's condition, electrocardiogram and blood pressure but also ultrasound examination of the heart with registration of left ventricular contractility before the load on the bicycle ergometer and immediately after the load termination. Indications for the study are determined by a cardiologist..
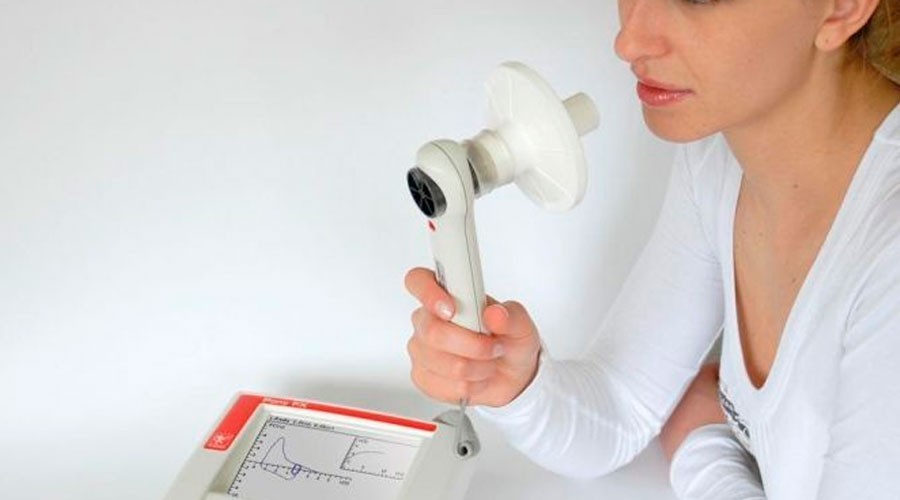 Spirography is the most common method of studying lung ventilation. It is of great importance in the comprehensive examination of patients suffering from diseases of the lungs and bronchi. It makes it possible to identify the presence of respiratory failure, determine its type, nature and severity, track the dynamics of changes in the state of the bronchopulmonary tree during the development of the disease and evaluate the result of treatment.
Spirography is the most common method of studying lung ventilation. It is of great importance in the comprehensive examination of patients suffering from diseases of the lungs and bronchi. It makes it possible to identify the presence of respiratory failure, determine its type, nature and severity, track the dynamics of changes in the state of the bronchopulmonary tree during the development of the disease and evaluate the result of treatment.

